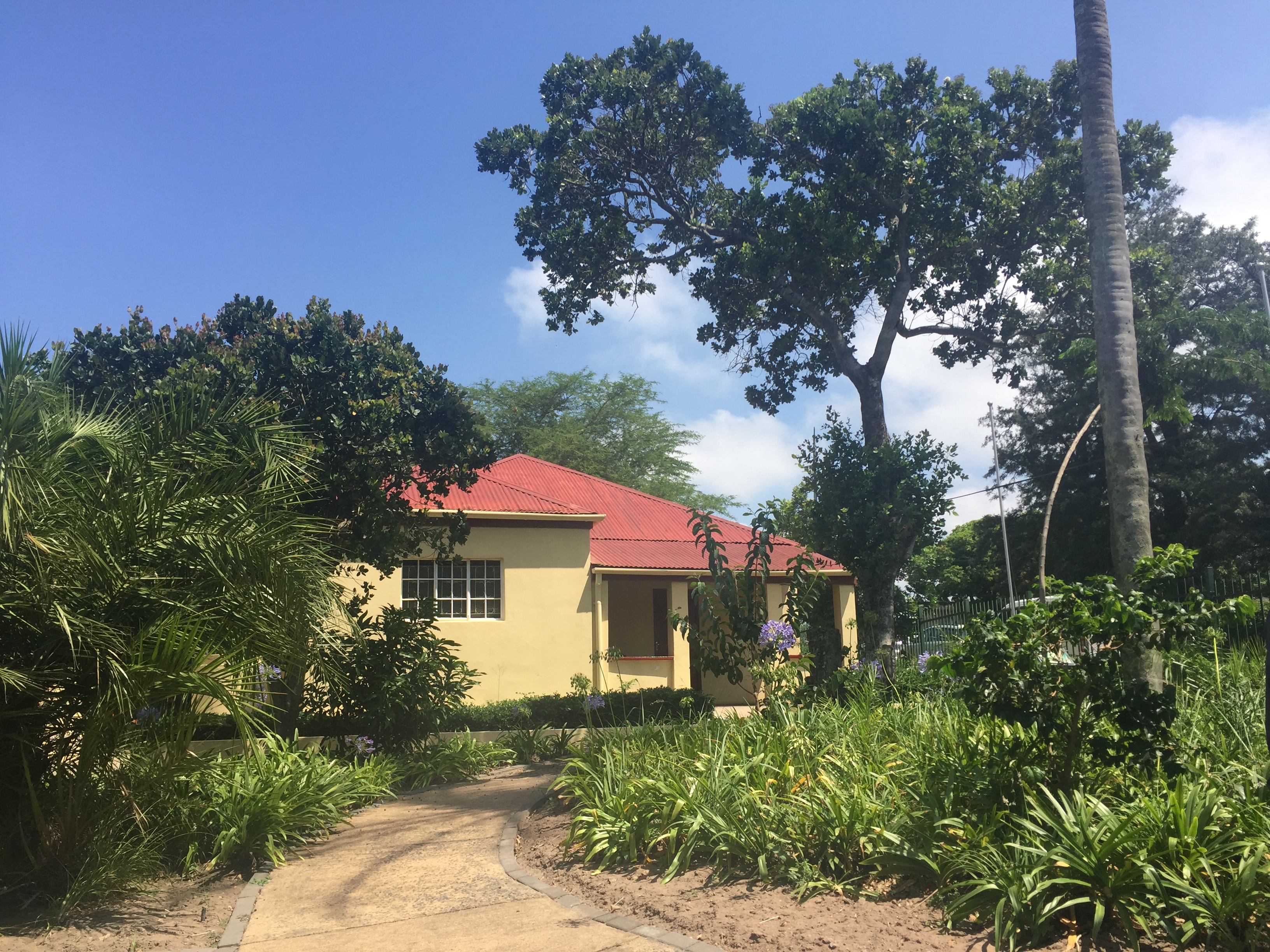
A visit to the Luthili Museum prompts a reflection on the history of the African National Congress (ANC) by preserving the legacy of its ninth president, Chief Albert John Mvumbi Luthuli. Chief Luthuli served as the ANC President from 1952-1967 and is celebrated for his commitment to opposing white minority rule in South Africa through peaceful means and organised resistance.
the legacy of its ninth president, Chief Albert John Mvumbi Luthuli. Chief Luthuli served as the ANC President from 1952-1967 and is celebrated for his commitment to opposing white minority rule in South Africa through peaceful means and organised resistance.
The museum was built on the grounds of Chief Luthuli’s original home in Groutville, KwaZulu-Natal. It first opened its doors in 2004 and is funded by the Department of Arts and Culture. The original structure of the house has been preserved and just down the road lies the church where Chief Luthuli’s gravesite lies.
In 1936, Luthuli, who had been working as a teacher, was elected chief of a Zulu tribe in Groutville. In 1945, he joined the ANC, just three years before the National Party came into power and began to implement the disenfranchisement policies for which it would become notorious. Chief Luthuli motivated the party to pursue peaceful means of resistance. When he was elected ANC president in 1952, the National Party government refused to allow him to hold both the presidency and the title of chief. Though the government revoked his chieftainship, the community resisted and continued to view him as their leader.
During most of the time that Chief Luthuli served as ANC president, he was banned by the government from leaving the Groutville district under the Suppression of Communism Act. Even 
Chief Luthuli died in 1967 while he was still serving as ANC president. Though the formal report on his death states that he was hit by a train near his home, both the autopsy of the body and context of his death suggest that story to be unlikely. There continue to be calls to re-examine his cause of death as many believe that it was a planned attack by the Apartheid government.
Today, Chief Luthuli is regarded as one of the key contributors to South African democracy. He advocated for a bill of rights and believed a constitutional court would uphold the ideals of the nation. Though he died before either were realised, his work paved the way for the ANC leaders who succeeded him. Today, the ANC headquarters in Johannesburg bears the name of Luthuli House in his honour.